SURGERY |
||
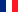
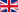
Cautery (3b) by PAQUELIN |
||
Burners are generally devices for the destruction of body tissues by incandescent heat. This causes, applied to surfaces volatile, different degrees of burns, which were brought about in the elderly medicine for the derivation of inflammation by the moxa. However, the incandescent heat also caused rapid hemostasis through the formation of a stuck scab, safe destruction of malignant tumors or infected tissue, and allowed bloodless tissue to be cut bloodlessly. Therefore, bleeding sites of the nasal mucosa, the inner surface of the uterus (!) Burned by burners, wounded by poisonous snakes or wounded dogs wound burned, blood-rich tissues, especially in gynecological operations and liver and lung operations, with the burning apparatus. In 1876, the French physician Claude André PAQUELIN (1836-1905) published a thermo-cautery with a platinum tip internally filled with very finely dispersed platinum moor, which, after being heated once, glowed, and through a gas-air mixture (supplied by a blower) (or other flammable vapors) could be kept glowing. *The discovery of the catalytic effect of platinum moor goes back to the pharmacist Johann Wolfgang DÖBEREINER (1780-1849). In 1816 he had succeeded in the oxidation of alcohol to acetic acid with the help of platinum moor. A few years later, he succeeded in igniting an oxyhydrogen gas mixture under the influence of platinum sponge one of the most important discoveries of early catalytic chemistry. It led to the invention of Döbereinerschen platinum lighter, which became a coveted commercial object. Textbook by Paquelin, purchased in 2005 from a dealer in Juan-Les-Pins. |